1. Intro
The goal is to understand the world from a geography perspective. Understand and explore some of the most unique scene and culture (just a little bit)
Plan: from North America to South America. Then Europe, Africa. Then Asia. Finally Polar region
2. Basic
Definition: Study of places and the relationships between people and environments
- Physical properties of the Earth
- Human societies spread across it
Principle: spatial perspective, holistic approach, scale(local global)
2.1. Tectonic Plates
The crust is divided into several pieces, float on semi-fluid asthenosphere
Interaction: move toward, move away, slide past
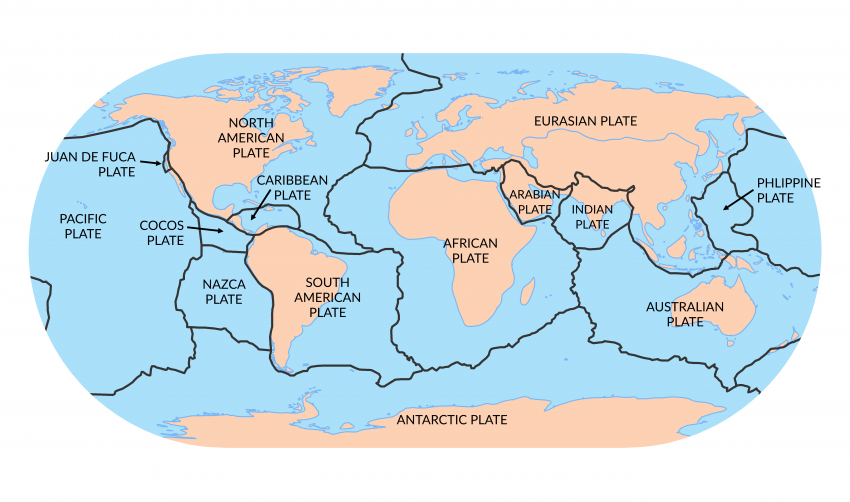
2.2. Mountain Formation
Primarily due to tectonic activities
Type: fold mountain (Himalayas), volcanic mountain (Fuji), block mountain (Sierra Nevada), plateau mountain
2.3. Rivers
Begin as small stream in mountains, gather more water from rainfall, other stream and ground water
Crucial for human civilization
2.4. Deserts
Cause: cold ocean currents or rain shadow
Type: hot and cold
2.5. Ocean
Ocean floor as varied as the continents
2.6. Volcanoes
An opening in the Earth’s surface, allowing hot magma and gases to escape
Most of the world’s active volcanoes are found on the Pacific Ring of Fire
2.7. Atmosphere
Multiple layers, we live in troposphere
Different climate zone
3. North America
3.1. Mountain
- Rocky: New Mexico up through western Canada and into Alaska
- 50-80 million years ago, plate
- Appalachian: Eastern US, from Georgia to Maine and on into southeastern Canada
- 480 million year ago, oldest mountains, place collided
- Sierra Madre: primary mountain range in Mexico
- 65 million years ago, volcanic activity and tectonic uplift
3.2. River
- Mississippi-Missouri River system: one of the world’s longest river
- Rio Grande: act as natural border between US and Mexico
- St.Lawrence River: connect the Great Lake and Atlantic Ocean
3.3. Coastlines
- East: mix of sandy beaches
- West: cliffs and rugged coastlines
- Gulf: along the Gulf of Mexico
3.4. Facts
Death Valley is the lowest point in North America
Great Lake is the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world by total area
Water distribution:
- Ice gap: 68.7%
- Ground water: 30.1%
- Surface: 1.2%
- River: 0.0002%
4. South America
Amazon Basin: primarily in Brazil and Peru, world’s largest river basin
Home to Amazon rainforest, largest tropical rainforest, produce around 20% of the world’s oxygen
Biodiversity: millions of species of flora and fauna, yet to be discovered
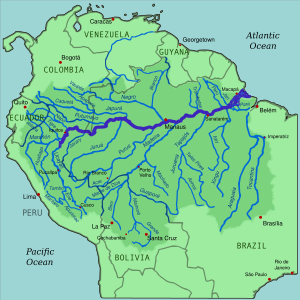
Andes Mountains: longest mountain range, stretch for over 7000 km along the western edge of South America
- Volcanoes: contain numerous active volcanoes within the Pacific Ring of Fire
- Play a crucial role in regional climates
Patagonia: southernmost part of South America
- East part: flat, arid steppes; West part: dense rainforests, glaciers
4.1. Country
Brazil: housing the majority of Amazon Rainforest
- Vast Pantanal wetlands
- Highlands of the Brazilian Plateau
- Tropical coastline of Atlantic forest
Argentina: Patagonia
Peru: Incan history
- Machu Picchu
- Coastal desert
Chile: slim nation, has the driest desert, Atacama
Colombia: Pacific and Caribbean coastlines
Venezuela: known for Orinoco River
- Has the highest waterfall, height of 979 meter (Angel Falls)
5. Europe
5.1. Mountain
Ural Mountain: natural boundary between Europe and Asia
- 250-300 million years old
- Erosion has worn them down, lower than many other mountain
Alps: Central to Europe’s climate and history
- Mont Blanc: highest in Europe, 4807 meter
Pyrenees: natural border between Spain and France
Apennines: backbone of the Italian peninsula
5.2. River
Danube: Europe’s second-longest river passes through 10 countries, from Germany’s Black Forest to Black Sea
- Black Forest: dense forest so dark from far
Volga: Flowing entirely within Russia, Europe’s longest river, play a vital role in Russia history
Rhine: From Swiss Alps, emptying into North Sea
Lorie: France’s longest river
5.3. Countries
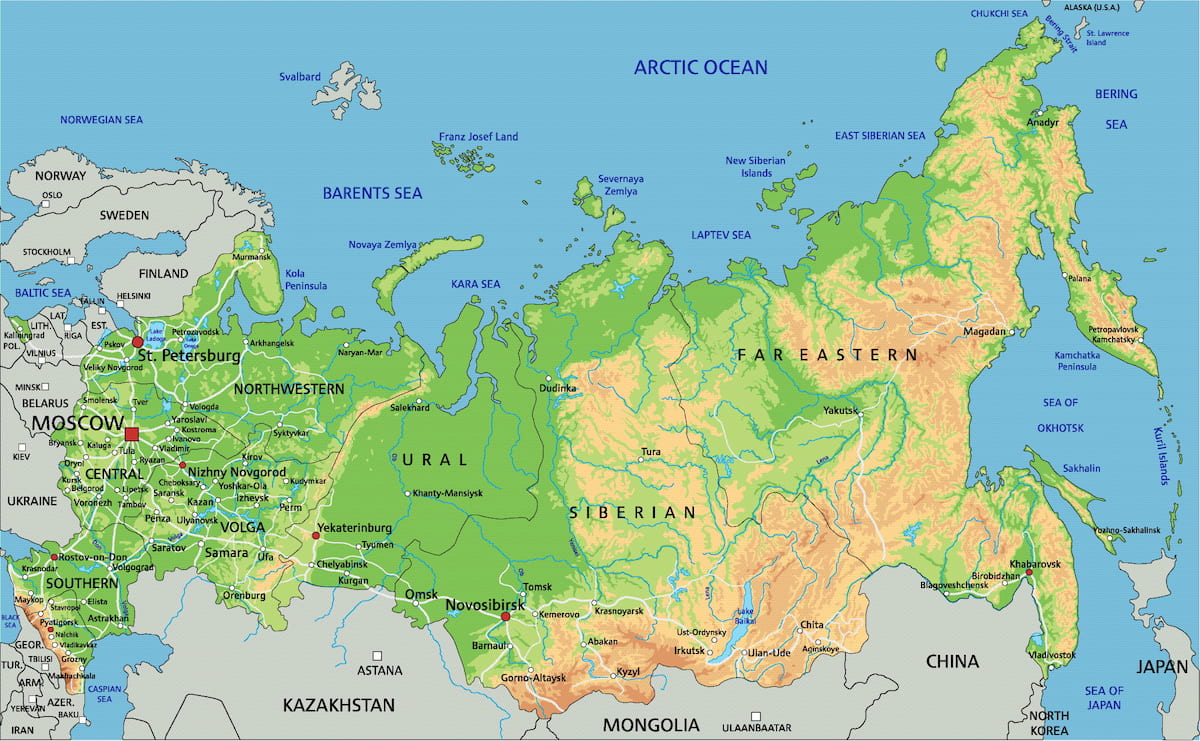
Russia
- West part in Europe, East part in Asia
France: diverse landscape from coastal plains and west to mountain ranges
Germany: uplands in center, lowlands in the north, Rhine, run through western Germany
6. Asia
6.1. West and South Asia
Himalayas: Spanning across five countries: India, Nepal, Bhutan, China and Pakistan
- Name come from Surveyor General of India
- Vital role influencing the climate of South Asia, acting as the barrier to cold Central Asian winds.
Ganges Basin: centered around Ganges River, most fertile and densely populated areas in the world
Arabian Peninsula: the largest peninsula in the world
- Predominantly desert, Empty Quarter, the largest continuous sand desert in the world
- Significant oil reserves
- Ancient shallow sea, organic material accumulation, sedimentation, chemical transformation, ideal rock structure, tectonic activity, preservation
- Historically significant as the birthplace of Islam
- Countries
- Saudi Arabia: 1932 by Abdulaziz Ibn Saud
- Yemen: North 1918, uniting 1990
- Gulf States: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, all British protectorates
6.2. Question
Emirate: political territory ruled by an emir
- A title of high office, similar to “prince” or “duke”
Saudi: Al Saud is the name of the ruling royal family
- Connection to Al Saud dynasty
- The foundation is closely linked with religious movement known as Wahhabism
6.3. Central Asia
Kazakhstan: largest landlocked country
The Steppes: stretch across the region, providing grazing land for livestock and serving as historical routes
Stan? Of Persian origin and means “land”
6.4. East and Southeast Asia
Yangtze Basin: stretching 6300km, the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the World
- Most important agricultural areas, producing rice, wheat, and cotton
- Home to numerous species
Plateaus of Tibet: the Roof of the World, highest and largest plateau, average elevation exceeding 4500 meters
- Harsh climate, low oxygen level
- Unique culture influenced by Tibetan Buddhism
- Geologically connected with Himalayas
Mekong Delta: where Mekong river empties into the South China Sea
- The rice bowl of Vietnam, major agricultural area, producing about half of Vietnam’s total agricultural output
Indonesia: world largest archipelago, consisting of over 17,000 islands
- Numerous ethnic groups since archipelagic nature, isolated communities developed independently
- Tectonic plates meet, sea level changing leading to volcanic activity and formation of islands
6.5. North Asia
Siberia, vast region known for its harsh climate, taiga forest, extensive river system
- Extremely code
- Rich in natural resources including oil, gas, mineral
- Originating of Samoyed dog
7. Australia
Great Barrier Reef: northeast coast of Australia in the Coral Sea
- Largest coral reef system, spanning over 2300 km
Outback: 内陆
- Vast, remote interior region of Australia
- Harsh climate
New Zealand
- North Island: know for geothermal activity, Auckland located on the North Island
- South Island: more mountainous, renowned for outdoor and adventure activities
Fiji: known for stunning coral reefs
Samoa: Feature lush rainforests, steep mountain
8. Africa
Sahara: stretch across North Africa
- The world’s largest hot desert, sand dunes, rocky plateau
- Extremely arid, temp can reach up to 50 C
Great Rift Valley: 大裂谷, a trench from Asia to Southeast Africa
- Created by tectonic plate movements, Africa and Somali divergent
- Encompass some highest and most stunning mountains, deep lakes
- A rich area for paleontological studies
Nile River: 6650 km, world’s longest river
- Play a crucial role in the civilization of Egypt and Sudan
Congo Basin: the catchment of Congo river
- World’s second-largest rainforest, rich in biodiversity
Mount Kilimanjaro: Tanzania, highest peak in Africa, 5895 meter, highest free-standing mountain
- Unique climate zones ranging from base to summit, rainforest, alpine desert, arctic summit
- Stratovolcano, formed by repeated layers of lava flows, volcanic ash
8.1. Country
Egypt: majority of the population concentrated along its bank
- Sahara desert cover most of Egypt
South Africa: features a wide variety of landscape, rich in minerals
Nigeria: most populous country in Africa
Kenya: dominates the geography with stunning landscapes and geothermal energy
Congo:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: unstable, conflict, poor
- Republic of the Congo: stable, rich
9. Polar Regions & Unique Geographical Phenomena
Antarctica: surrounded by massive ice shelves
- Ross and Ronne are two of the largest
- Mountain:
- Transantarctic Mountains, divide into East and West
- Ellsworth Mountain contain highest peak, Vinson
- Climate: contain 60% of the world’s fresh water
Arctic: considerably smaller than Antarctic
- Mountain: Brooks, Scandes, Urals
- Climate: global air conditioner
- Resources: has significant reserves of oil
10. Plan
Day 1: Introduction & North America
- First 20 minutes: Overview of Earth’s geography: tectonic plates, mountain formation, rivers, etc.
- Next 40 minutes: Dive into the physical geography of North America: Major mountain ranges, rivers, climates, and coastlines. Touch on USA, Canada, and Mexico’s significant features.
Day 2: South America
- First 20 minutes: Revisit major North American geographical features for reinforcement.
- Next 40 minutes: Detailed look at South America’s physical geography, focusing on the Amazon Basin, Andes Mountains, Patagonia, and touching on the significant features of major countries.
Day 3: Europe
- First 20 minutes: Brief recap of South American geography.
- Next 40 minutes: Delve into Europe’s physical geography, covering the Ural Mountains, Alps, major rivers like the Danube and Volga, and focusing on the geographical distinctions of countries like UK, France, Germany, Russia, etc.
Day 4: Africa
- First 20 minutes: Revisit key European geographical features for reinforcement.
- Next 40 minutes: Explore Africa’s physical geography, focusing on the Sahara, Great Rift Valley, Nile, Congo Basin, Mount Kilimanjaro, and understanding the geographical distinctions of countries like Egypt, South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya.
Day 5: Asia (West, South, & Central)
- First 10 minutes: Brief recap of African geography.
- Next 25 minutes: West and South Asia’s physical geography, focusing on the Himalayas, Ganges Basin, Arabian Peninsula, and discussing countries like Saudi Arabia, India, and Pakistan.
- Next 25 minutes: Central Asia, touching on the major countries and the significant features of the region such as the Pamir Mountains and the vast steppes.
Day 6: Asia (East & Southeast) & Oceania
- First 20 minutes: Revisit the geography of West, South, and Central Asia for reinforcement.
- Next 20 minutes: East and Southeast Asia’s physical geography, exploring the Yangtze Basin, Plateaus of Tibet, Mekong Delta, and discussing countries like China, Japan, and Indonesia.
- Next 20 minutes: Dive into Australia’s major physical features, including the Great Barrier Reef, the Outback, and the island nations of Oceania like Fiji, Samoa, and Papua New Guinea.
Day 7: Polar Regions & Unique Geographical Phenomena
- First 20 minutes: Antarctica and Arctic regions’ geography, understanding their ice shelves, mountain ranges, and significance in global climate.
- Next 40 minutes: Dive into unique global phenomena, emphasizing prominent mountain ranges, major rivers, key deserts, and other unique geographical formations across continents.