1. Intro
Free online first aid course - First Aid for Free
Know the basics to treat daily life injuries
Some of the most common injuries in daily life
- cuts. scrapes
- burns
- choking
- nosebleed
- animal bites
Basic Skill
- CPR, AED
- Wound case
- Burn treatment
2. Introduction
Three Ps
- Preserve Life
- Prevent Deterioration
- Promote Recovery
Incident management
- you are the most important person and your safety come first
- Report to 911
- Location / number of victim / nature of injuries
Infection Control
- Hand Hygiene: wash your hands
- Personal protective equipment
- clinical waste: disposed appropriately
3. Unconscious Victim
Primary survey: DRAB
Danger: make sure the scene is safe
Response: attemp to wake the person up by shouting loudly in both ear, gently shaking
- if unconscious, they lose muscle tone, tongue might block their airway
Airway: tilting the head backwards and lifting the chain
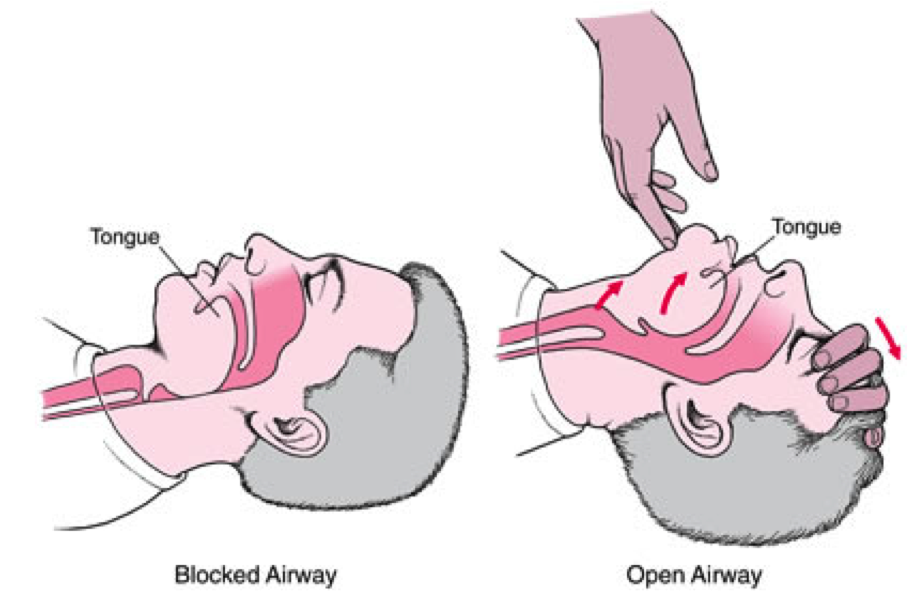
Breathing, it should have normal breathing for 10 seconds
If normal breathing, the next step is place into recovery position

If not breathing, do CPR: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- without oxygen, brain cell starts to die in 4-5 minutes
- CPR will not restart someone’s heart, just keeps them alive until a defibrillator arrives
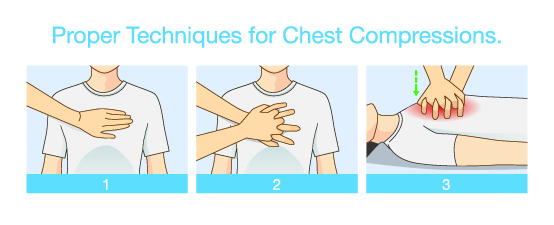
CPR: Chest compression are the most important component of high-quality CPR
- Press 5-6 cm, release all pressure without losing contact
- Repeat 100-120 chest compression per minutes
- It’s common feel ribs break, still need to deliver high-quality chest compression
4. Bleeding and Shock
The circulatory system, average adult have around 5 liters of blood
Three types of blood vessel
- Arteries, high pressure, spurt out 动脉
- Veins, 静脉, low pressure, flow steadily
- Capillaries: very small and low pressure, will ooze
Steps
- Expose injury and elevate above level of heart
- apply firm direct pressure over wound
- call for emergency medical help
Puncture wounds
- Do not remove the object unless it is very small
- Apply pressure around the wound
- Elevate the limb to prevent further blood loss
Shock: caused by sever blood loss
- Recognize: pale, confusion, fast/weak pulse, fast shallow breathing
- First aid: liw the casualty down and raise legs if possible, keep them warm
- Do NOT give anything drink or eat
Minor wounds
- Wash hands, wear gloves
- Clean the wound thoroughly with antiseptic or clean running water
- Cover the wound using a clean dressing
5. Burns and Scalds
Classification
- Type
- Scald, by hot liquid
- Friction, by rough surface
- Radiation
- Electrical
- Chemical
- Depth
- Superficial
- Partial thickness
- Full thickness
Palm 1% surface. Burns more than 10% is serious and may produce shock
Steps for minor burn
- Run the burn under cold running water for a minimum of 10 minutes
- Goal: cool the burn
- Expose the affected area
- Cover with non-fluffy covering
What NOT to do:
- do not try to remove clothing sticking to a burn
- do not apply toothpaste to a burn
6. Question
Cold/warm?