1. Intro
Combine ICP and point-to-plane ICP into a single probabilistic framework
- More robust to incorrect correspondence
- Easier to tune the maximum match distance
2. How it works
Align two point sets in 3D space
- by minimizing the distance
- Extends ICP by allowing more general types of correspondaences
3. Standard ICP
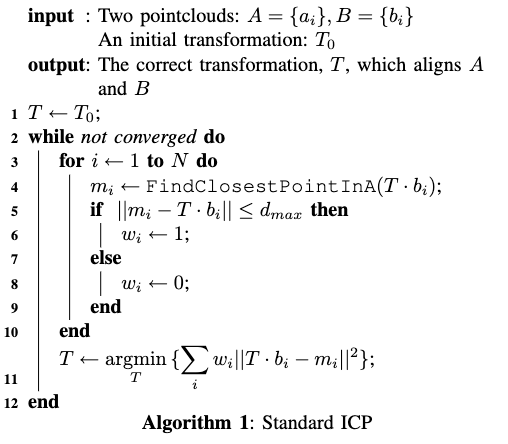
4. Point-to-Plane
Update the T calculation process (Line 11)
$$
T \leftarrow \underset{T}{\operatorname{argmin}}\left{\sum_i w_i\left|\eta_i \cdot\left(T \cdot b_i-m_i\right)\right|^2\right}
$$
Taking the surface normal information
5. GICP
Also improved the Line 11
Attaching a probabilistic model
- Correspondence: computed with Euclidean distance
- Use of KD-tree and speed up
6. NDT?
NDT represents the entire point cloud as a collection of Gaussian distributions.
- divide the 3D space containing the point cloud into a grid of cells
- Each cell that contains at least one point is then represented by a Gaussian distribution
- iteratively revises the transformation (translation and rotation) to minimize the difference between the two point clouds.