1. Meshroom
Photogrammetry is the science of making measurements from photographs. It infers the geometry of a scene from a set of unordered photographies or videos. Photography is the projection of a 3D scene onto a 2D plane, losing depth information. The goal of photogrammetry is to reverse this process.
The dense modeling of the scene is the result yielded by chaining two computer vision-based pipelines:
“Structure-from-Motion” (SfM) and “Multi View Stereo” (MVS).
2. Pipeline
- Feature extraction
- Goal: extract feature points
- Method: SIFT
- Image matching
- Goal: find images looking to the same area, then we can reduce computation
- Method: Vocabulary tree approach
- Feature matching
- Goal: match feature points between candidate image pairs
- Method: calculate distance and use RANSAC
- Structure from Motion (SFM)
- Goal: compute the pose of each images
- Methods:
- Fuse all matched feature point pairs
- Choose the best initial image pair
- Compute the fundamental matrix
- Using PnP to calculate the pose
- Filter the results using Bundle Adjustment
- Depth Maps Estimation
- Goal: get the depth value of each pixel
- Method: Semi-Global Matching
- Meshing
- Goal: create geometric surface representation of the scene
- Method:
- Fuse all depth maps into global octree
- Perform 3D Delaunay tetrahedralization (四面体化), then voting
- Graph cut Max-Flow, optimally cut the volume
- Texturing
- Goal: texture the generated mesh
- Method:
- Compute UV maps
- For each triangle, use the color of each candidate to estimate
3. Data Acquisition
Goal: Clear images from different angles
Camera setting
- Fixed low ISO (low noise)
- Fixed high shutter speed (less then 1/100s, no blur)
- Fixed long focal length (everything is in focus)
- Fixed white balance (stable image color for feature matching)
- Enough lighting (so that we can keep low iso and high shutter speed)
Move:
Camera fixed, object move
will need a spin base
keep the background pure color
Camera move, object fixed
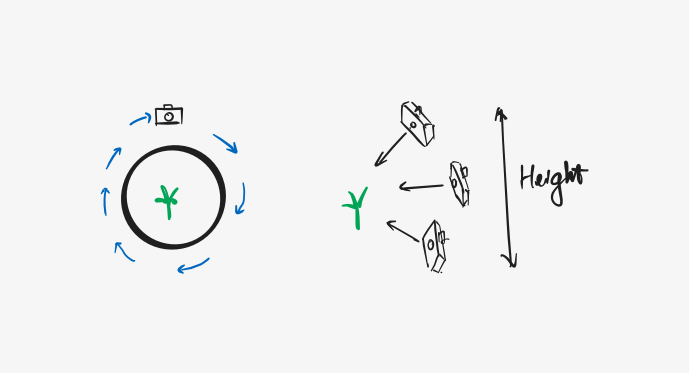
Shot around the object (360 degree)
In each spot, shot from 3 different heights
Illustration:
4. Results
The final results of Meshroom is pretty unstable
- In many cases, even high quality images dataset can not generate satisfied results
- However, when the algorithm works, it can generate detailed mesh and texture.
5. Discussion
Why performs bad?
I think the main reason is the object itself. For the leaf object, it has a few features that make the algorithm doesn’t work
- The leaf is so thin. It’s hard to generate a plane using point cloud
- The leaf is semi-transparent, it will look differently from different angle
- The leaf skin is so smooth that would generate reflection
How to solve the problem? (Possible solution)
- Using laser to generate point cloud (to capture textureless feature)
- Create great lighting system, try to avoid reflection and semi-transparent situation