1. Intro
Path tracking for car-like robot
Or can be called as vehicle lateral control
Some most common method
- PID control
- Stanley controller, based on cross-track error and heading error
- Pure pursuit, based on current position and a point
- Model predictive control(MPC), use a model of the vehicle dynamics to predict the future behavior, then optimize the control input
- Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR), use a linearized model to calculate the optimal control input
2. Compare
| Method | Pro | Con |
|---|---|---|
| PID | simple good for linear system |
stability issue |
| Stanley | simple capable |
sensitive to parameter tuning not good with sharp turn |
| Pure Pursuit | simple good for low speed |
suffer from oscillation |
| MPC | capable, optimize | Computationally expensive |
| LQR | optimize | linearized model |
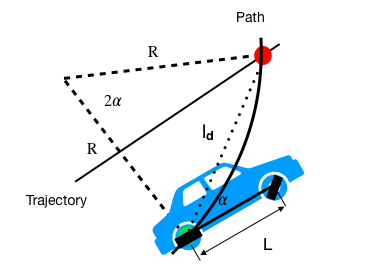
3. Pure Pursuit
Geometric path tracking controller
Look ahead point: A fixed distance on the reference path ahead of the vehicle
Reference point of vehicle: the center of rear axle
Target point:
4. Stanley Controller
CTE: cross-track error
Reference point of vehicle: the center of front axle
Cost: heading error + cross-track error
Control logic
- Eliminating the heading error
- Eliminating the cross-track error
- Clip the steering to bond
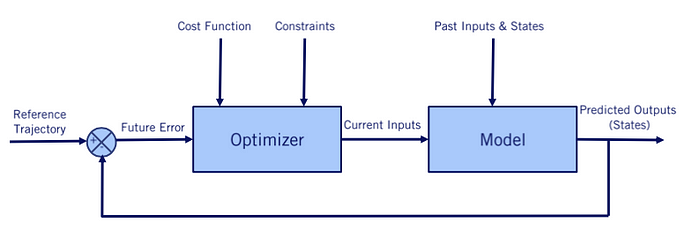
5. MPC
Define the cost function
- deviation from the reference path
- control command magnitude
Predict the future evolution of the system:
- update the system state
- x, y, $\theta$, $\delta$