1. Intro
Basic Method
- Graph-based: A*, D*
- Anytime Sampling: RRT, RPM
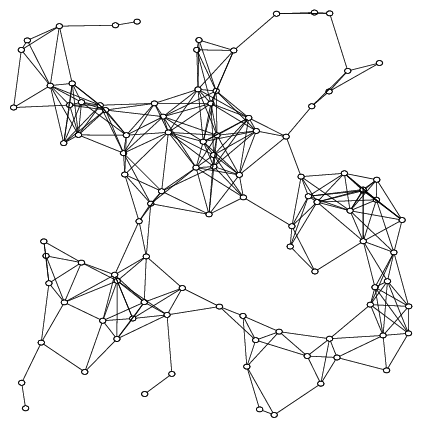
BIT: combine graph and sampling
- Use RGG to approximate the searched space
Prove
- Completeness: can always find a solution from start to goal (if exist)
- Almost-sure Asymptotic optimality
2. Unknown Term
RGG: random geometry graph
- A type of mathematical graph
- Node is randomly distributed in geometric space
Lebesgue Measure
- Assign a numerical value to a subset of euclidean space like line/plane/space
- Generalize the notion of length/area/volume
- Use more advanced math tool like calculus and analysis
LPA: lifelong planning A*
- designed to work in dynamic environment
- incremental update
- Maintain two sets of node
- open: have been generated, not yet expanded
- closed: have been expanded
- Each node has two value
- g: the actual cost
- rhs: the heuristic estimate
3. Algorithm
Idea:
- Find a solution from start to goal, form a batch
- In the next batch, form denser RGG