1. Goal
Understand how a Chip made
2. Silicon
special and important to Semiconductors
By introducing different thing, we can control the flow of electricity
Transistor: amplifies and switches electrons
- Chip is just countless assemble of transistor
- can store and operate information
3. Ecosystem
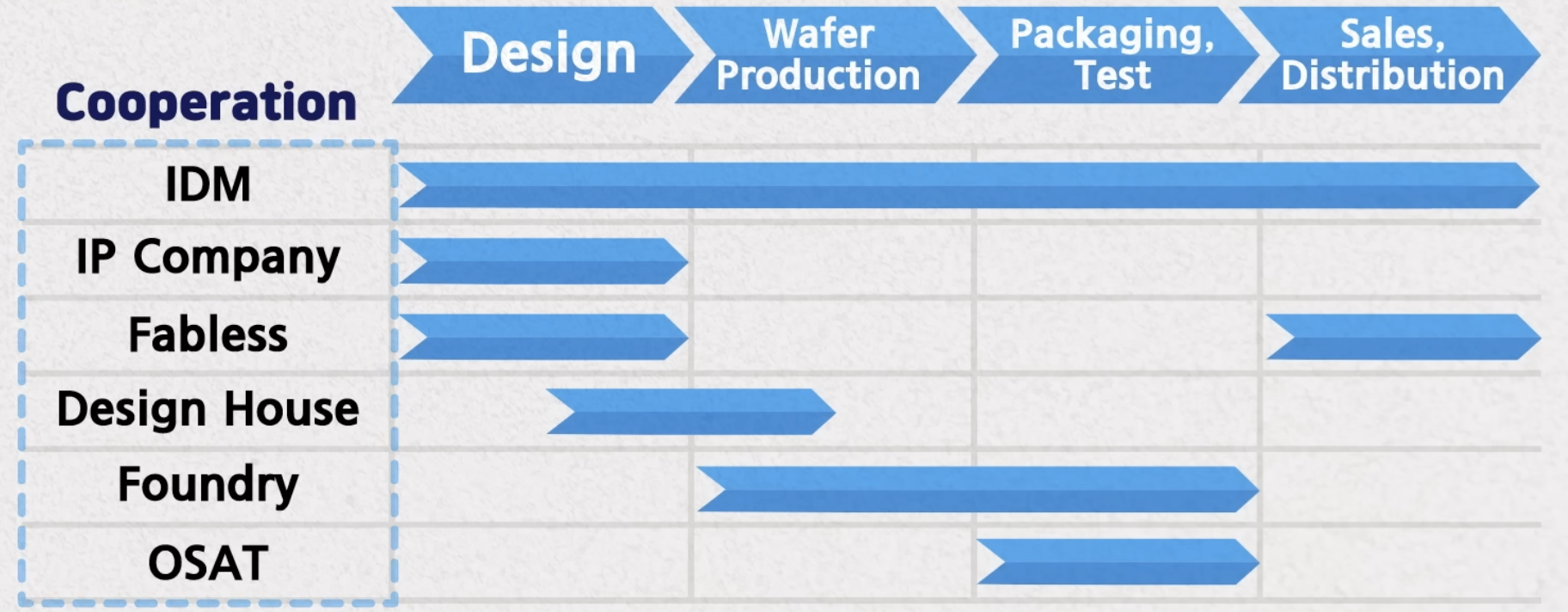
Group
- IDM: do both
- Foundry: only produce
- Fabless: only design
- Design housr: connect fabless and foundry
4. Manufacture Process
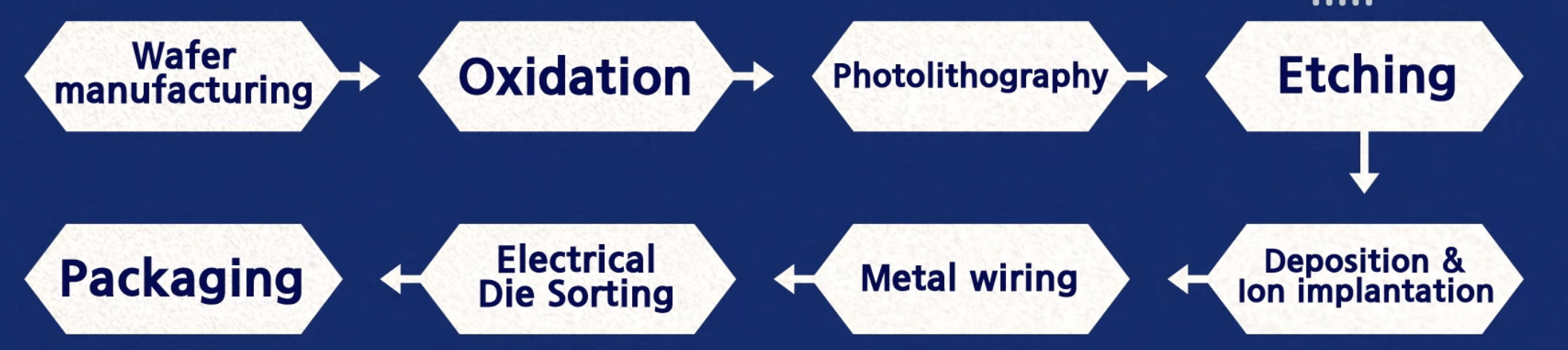
Wafer is not conductive yet
Oxidation: protection

Photolithography
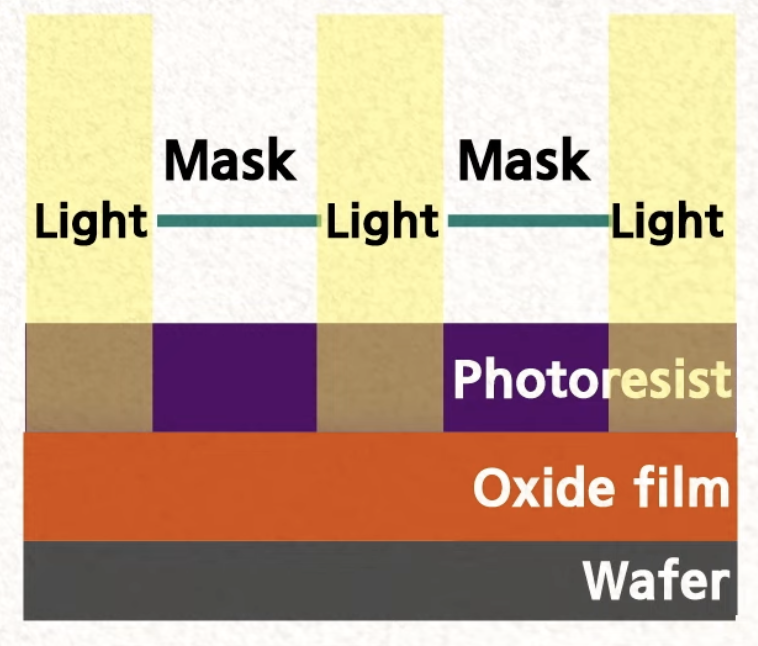
Etching: remove unwanted oxide film
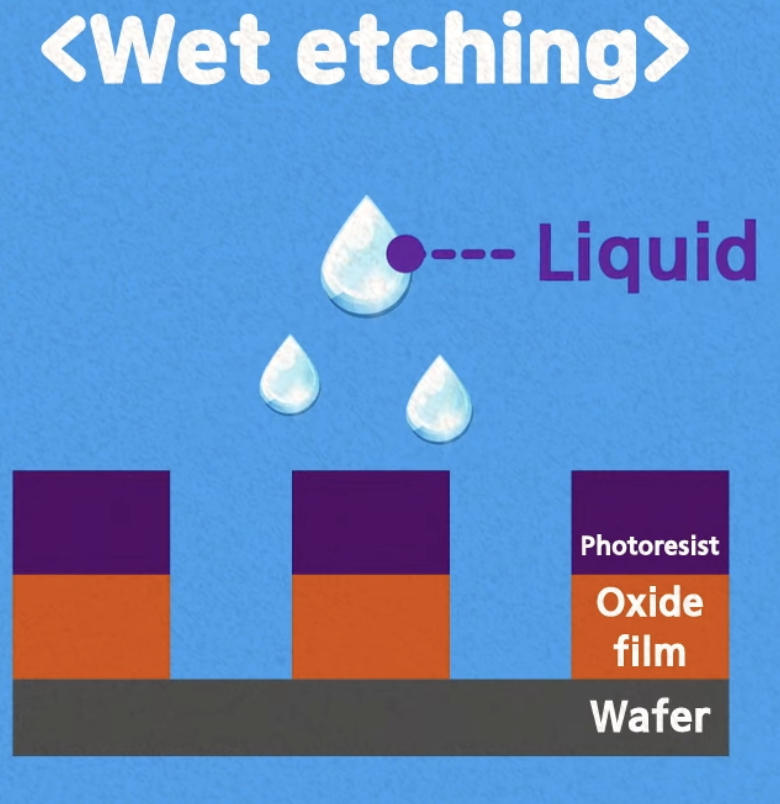
Deposition, Ion Implantation
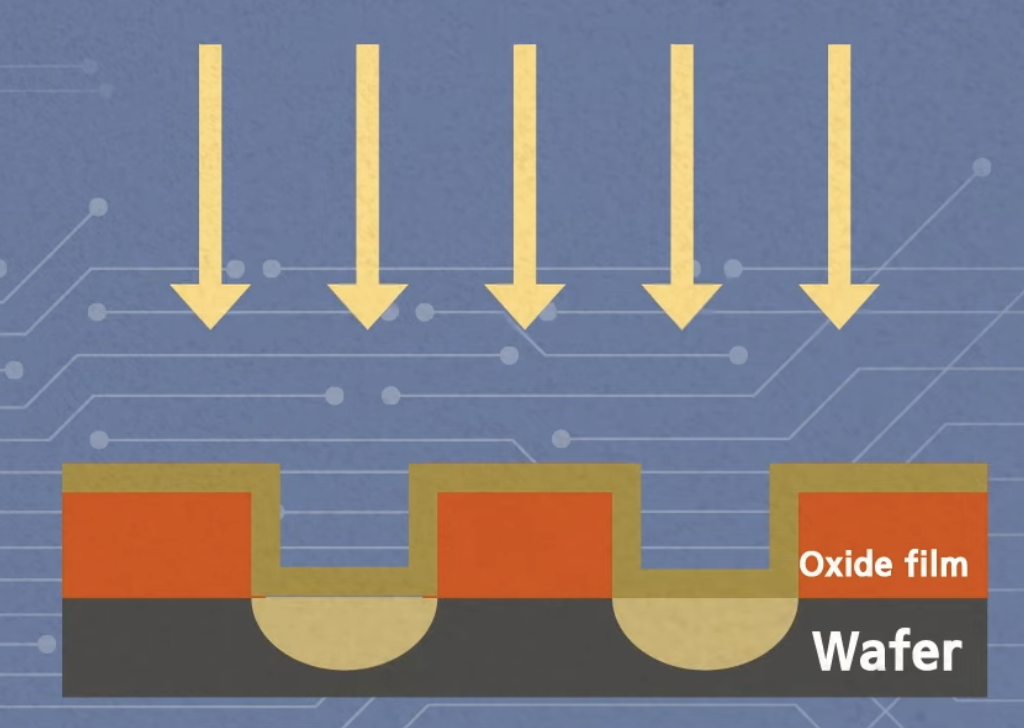
Now wafer become conductive
Metal Wiring

5. Memory
Two type
- Volatile: DRAM
- lost data after power off
- Faster processing speed
- Non-volatile: NAND
- Permenant save
5.1. DRAM
Dynamic Random Access Memory
- Cell
- Transistor: controller
- Capacitor: 0/1
- Need refresh some time
Cell get smaller, the capacitor would leak
DDR: Double Data Rate
- DDR5 further speed
5.2. SSD
HDD: magnetic disk spinning
SSD: no motor, faster speed
Like a computer
- A controller like CPU
- A DRAM like ram
- A NAND Flash like disk
- Most important
NAND
- SLC: 1, best but most expensive
- MLC: 2
- TLC: 3
- QLC: 4
6. System Memory
CPU / Mobile AP
SoC: system on chip
NPU: Run deep learning model
Sensor, DDI: capture, display
PMIC: power management
7. Sensor
High Resolution Problem:
Since the pixel size is too small
- light leak
- higher noise
8. Power Management
All parts use different voltage
PMIC control the battery usage
Different part need different PMIC like 10-20
- CPU
- Display
- …
9. How SSD works
Garbage collection: ensure the cell earsed time are similar
Loading data from QLC would increase error
The temperature would influence the data saved.
- The controller would store the temp
10. Packaging
- Cutting: laser saw
- Attaching: lead frame
- Wiring, bonding
- Modling